Developing Next Generation EO Applications
The Company
RSS-Hydro is a Luxembourg-based company developing innovative water and climate risk solutions to help public sector and industry clients achieve impact in the SDGs for a better and safer future. We are regularly carrying out a number of research projects with national and international partners to develop science-based commercial solutions using the newest advances in Earth Observation (EO) and space technologies and combine this with numerical modeling and novel computing architecture. This allows us to push current state-of-the-art capabilities to the next level, so we can build next generation products and offer them today.
One of our flagship EO products that has now entered its commercialization phase, is FloodSENS, an AI-based algorithm that creates valuable flood impact maps even from clouded satellite images to support the financial risk industry as well as the international disaster response community.
Motivation for FloodSENS
The value of satellite sensors for mapping and monitoring floods has long been established and oftentimes during flood disasters satellites represent the only means of obtaining actionable information. Over just the last couple of years, under a strong climate risk signal and economic insecurities, we have witnessed disastrous flood events, spanning across unprecedented spatial and temporal scales. These disasters trigger humanitarian crises, massive asset damage and very often result in large displacements of people that cause security and conflict concerns. During such large events that are unmeasurable and cannot be monitored with traditional field equipment, satellites are one of the only means to gather crucial information for mitigation, response and recovery. Although SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) may be the obvious choice for detecting flooding during adverse weather conditions, the present archive of available SAR images is still rather small to infer trends about flood risk and climatology of floods whereas optical satellite sensors of various resolutions have been around for more than 50 years now, albeit hampered by cloud cover during floods. Nonetheless, there are many examples of flood disasters where optical satellite sensors have been providing cloud-free or partially clouded imagery.
The FloodSENS Algorithm
It is clear that overcoming the cloud cover issue in optical flood images would certainly be beneficial since it would allow a higher number of impacted areas to be mapped and it would also greatly extend the archive of flood maps from satellites, thereby providing better information to both the flood response sectors, including defense intelligence, as well as the financial risk industry, particularly the insurance and reinsurance sectors. To this end, RSS-Hydro has gathered needs and requirements from both the humanitarian and reinsurance sectors, and together with the UN WFP and Willis Towers Watson (WTW) as stakeholders, has joined ESA’s InCubed program to develop a Machine Learning (ML) application, called FloodSENS, to extract flooded area in optical flood images, whether cloud-free or partially clouded.
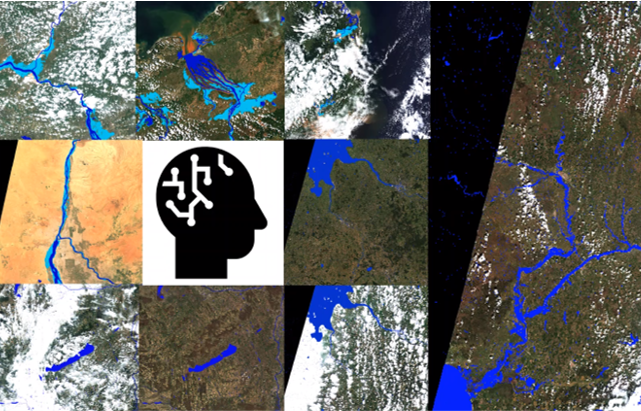
Example tiles of FloodSENS from different regions in the world.
The ML model is based on the well-known U-Net architecture and uses Sentinel-2 (S-2) flood images and derivative layers from digital elevation models relating to topography and waterflow to map flooding even below partial cloud cover. The algorithm further employs a squeeze and excitation network to extract information about the importance of the different input layers. During the project, FloodSENS was trained on a large number of expertly labelled S-2 flood images across different biomes, events and locations to ensure acceptable transferability, which is to become an important part of RSS-Hydro’s IPR of FloodSENS. Internal application testing and validation shows, unexpectedly, varying degrees of performance and accuracy. Overall, on average, FloodSENS performs at least as well as any robust and calibrated traditional band ratio index (>90% correct prediction), and in some cases outperforms such, and even maps below low cloud cover and correctly includes flood impact areas from dried out areas by following debris lines.
Moving to the Next Level of Implementation
Many exciting developments are happening in the new space sector, from smallsat SAR or thermal sensor constellations and satellite video to in space data relay systems and even in-orbit computing platforms.
Our growing international partner network, in which EARSC plays an important role, allows us to play a major part in these exciting developments with our EO applications that we thrive to improve with potential stakeholders in an agile development process.
One of our latest exciting developments includes the partnership we have with NVIDIA. We use various geospatial datasets with NVIDIA’s scene-generation platform Omniverse to build realistic 3D animations of disaster impact that help increase resilience of vulnerable communities.
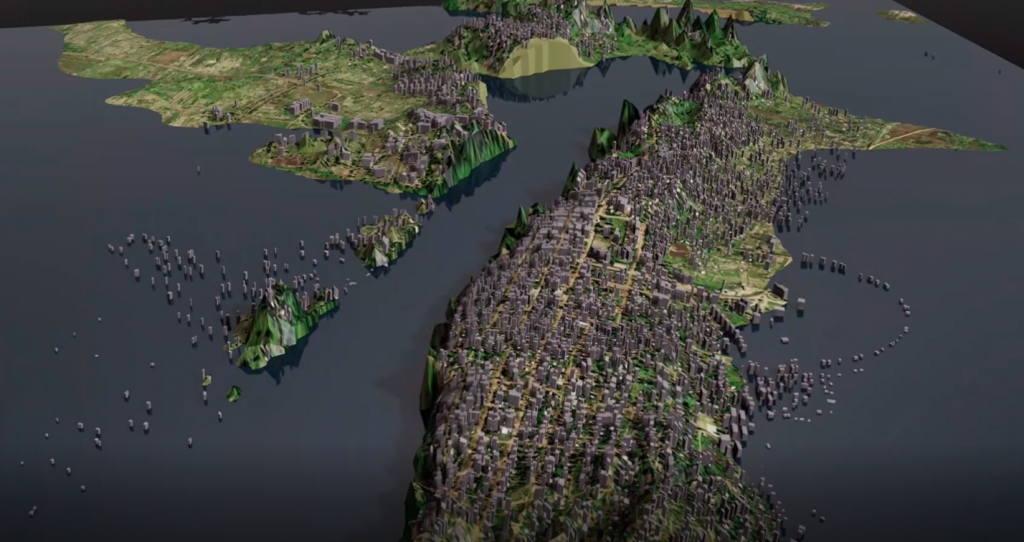
A snapshot scene from our own 3D animation creation using the Omniverse platform of the flooding in the coastal areas of Mozambique caused by the massive tropical cyclone Idai in March 2019, mapped with FloodSENS
From these partnerships and collaboration we, at RSS-Hydro, ensure that our products can seamlessly grow in value-add and market share potential.
“Together, let’s shape the future of the global EO market”
Contact
Visit our website: https://rss-hydro.lu/
Follow us on social networks: LinkedIn Twitter
Email us at: info@rss-hydro.lu
